The Amazing World of Flowering Plants
Starting Our Journey with Flowers
Have you ever stopped to look at a bright, colorful flower? Flowers are truly amazing parts of nature. They make our world beautiful. These flowering plants are found almost everywhere. They grow in gardens, fields, and even in the desert. Learning about them is a great adventure. We can discover how they grow and how they live.
The Special Name for Flower-Bearers
The special group of plants that make flowers are called angiosperms. This name comes from two Greek words. Angeion means “case” and sperma means “seed.” This is because their seeds grow inside a protective case. This case is often the fruit we eat. Every time you see a flower, you are looking at an angiosperm. These blooming plants are the most common plants on Earth.
What is a Blooming Plant?
So, what is a blooming plant? A blooming plant is simply any plant that produces a flower. The flower is the part of the plant that makes seeds. It is key for the plant’s reproduction. These plants use their flowers to attract animals. These animals help them make new seeds. These seeds then grow into brand new plants. This is the simple truth about plants that bloom.
The Most Common Plants on Earth
If you look around, most of the plants you see are the ones that flower. Scientists estimate there are over 300,000 different kinds. This makes flowering plants the largest group of plants. From tiny wildflowers to large oak trees, they are everywhere. They are essential to life on Earth. They give us food and also the air we breathe.
Key Features of Flowering Plants
Understanding Their Main Characteristics
Every type of plant has unique features. Flowering plants characteristics are what set them apart. The most important one is the flower itself. The flower helps them make seeds. Another key feature is that their seeds are enclosed. They are protected inside a fruit or seed pod. This protection helps the seeds survive. This lets more new plants start to grow.
The Role of the Flower
The main job of the flower is reproduction. It holds the plant’s reproductive organs. Flowers are often bright and smell sweet. This is a very clever trick of nature. It helps to attract insects and birds. These helpful visitors move pollen from one flower to another. The process of making seeds begins this way.
How Seeds Are Kept Safe
The seeds of these blooming plants are kept safe. They are covered by a part called the ovary. This ovary later ripens into a fruit. Think of an apple or a pea pod. The fruit protects the seed from danger. It also helps the seed travel to a new place. The fruit can be carried by animals or by the wind.
A Biological Definition for Flowering Plants
In a textbook, the flowering plants definition biology gives a formal explanation. They are known as Angiospermae or Magnoliophyta. They are vascular seed plants. Vascular means they have tubes to move water and food. They all make true flowers. This makes them different from non-flowering plants like pines. Pines make cones, not flowers.
The Structure of a Flower
The flower itself has several key parts. The colorful petals attract the helpful pollinators. The male part is the stamen, which makes pollen. The female part is the pistil, which catches the pollen. If you want to see how these parts fit together, you can look up a flowering plants diagram. This diagram will show you every tiny piece and its function.
How Flowering Plants Are Grouped and Named
The Science of Plant Classification
Scientists like to put plants into groups. This is called flowering plants classification. It helps us understand how they are related. Plants are first grouped by if they have one or two seed leaves. A seed leaf is the first leaf that comes out when a seed sprouts. This simple difference creates two major groups.
Monocots and Dicots
The two main groups are Monocots and Dicots. Monocots have only one seed leaf. Grasses, lilies, and corn are Monocots. Their flower parts usually come in groups of three. Dicots have two seed leaves. Roses, sunflowers, and beans are Dicots. Their flower parts are often in groups of four or five. This is a basic way to classify them.
What Flowering Plants Are Called
You might hear different names for these plants. As we learned, flowering plants are called Angiosperms. They are sometimes called “true flowers.” They are also often just called “blooming plants.” These names all mean the same thing. They tell you that the plant uses flowers to make seeds.
Looking at Specific Examples
It is fun to look at flowering plants examples to see the variety. The elegant rose is a famous example. So is the tall, bright sunflower. Apple trees and orange trees also produce flowers. Even the tiny, shy violet is a flowering plant. These examples show how different they all look. Yet, they all share that same basic trait: the flower.
Getting to Know Different Types
The huge variety of flowers means there are many types of blooming plants. We can group them by when they grow. Annuals live for only one growing season. Perennials live for many years. Biennials live for two years. Understanding these types helps gardeners plan their gardens well.
The Life of a Flowering Plant
Understanding the Life Cycle
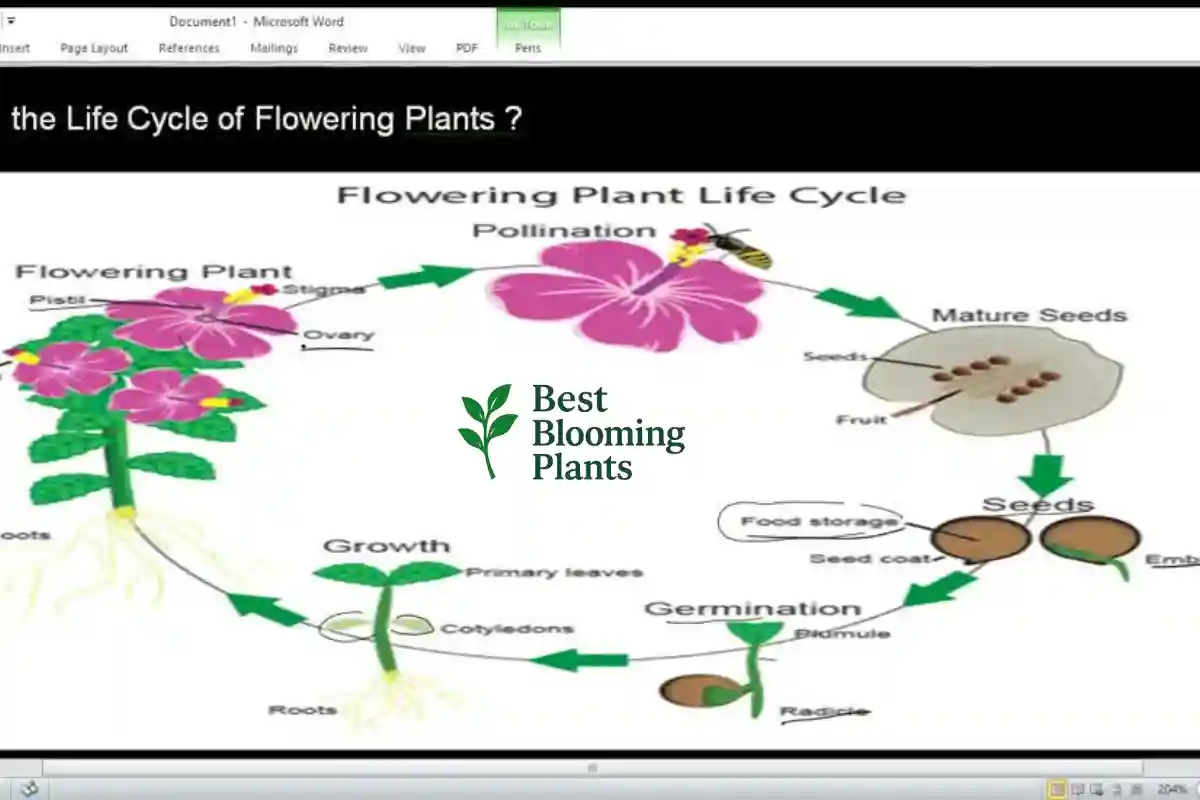
Every living thing has a life cycle. The flowering plants life cycle is very special. It shows how a plant grows from a seed. It then produces a flower. Finally, it makes new seeds. It is a continuous loop of growth and new life. This whole process can take a few weeks or many years.
Stage One: Seed and Sprout
The cycle starts with a seed. The seed needs water, warmth, and air to sprout. This is called germination. A small root pushes down into the soil. A tiny shoot grows up toward the sun. This little sprout is the start of a new plant. It needs sunlight to make its own food.
Stage Two: Growth and Green Leaves
The small plant grows bigger and stronger. It grows more leaves and a sturdy stem. The leaves are the plant’s food factory. They use sunlight and water to make sugar. This stage is all about getting ready to flower. The plant is getting energy to prepare to bloom.
Stage Three: The Time to Bloom
The most exciting stage is when the plants blooming. This means the flower buds open up. The plant is now ready to reproduce. The colors and scents are strong. This is when the plant works hard to attract its helpers. The beauty we enjoy is a key part of this stage. When you see plants bloom, you know life is continuing.
Stage Four: Making New Seeds
This stage is all about flowering plants reproduction. This happens after pollen moves from one flower to another. The pollen joins with the female part of the flower. This makes the seed. The flower parts then change and become the fruit. The fruit holds and protects the new seeds.
Reproduction: How Flowers Make More Flowers
The Secret to Plant Babies
Flowering plants reproduction is a beautiful natural process. It starts with the transfer of pollen. This transfer is called pollination. Pollen is a fine, yellow dust. It is the male reproductive part. Pollination is needed to start the seed-making process.
Pollination by Wind and Animals
Some plants rely on the wind to move their pollen. Grasses are a good example of this. Other plants rely on animals. Bees, butterflies, and hummingbirds are great pollinators. The flower gives them sweet nectar as a reward. As the animals drink, pollen sticks to them. They then carry it to the next flower they visit.
Fertilization and Seed Development
Once the pollen lands, it travels down to the ovary. This is called fertilization. A tiny embryo starts to form inside. This embryo will become the new plant. The wall of the ovary grows and turns into the fruit. This process shows how amazing nature is. Every seed is a promise of a new plant.
The Importance of Drawings and Diagrams
If you want to see exactly how this works, a flowering plants drawing can help. A simple drawing labels the parts. It shows the path of the pollen. It shows how the seed forms inside the fruit. These drawings help students learn complex steps. They make the process easy to understand and remember.
Types of Blooming Plants for Every Season
A Plant for Every Time of Year
Some blooming plants only flower in the spring. Others wait until the heat of summer. Some even bloom in the cold of winter. There are even flowering plants all season long in many places. This variety means gardens always have something beautiful to show. Gardeners love this diversity in bloom times.
Flowers for Spring and Summer
Spring is the time when many plants wake up. Tulips, daffodils, and hyacinths start to bloom early. Summer brings the heat and a rush of color. Roses, petunias, and sunflowers all come out. They take advantage of the long, bright days. They are a welcome sight in every garden.
Flowering Plants All Year Round
Some special varieties can be considered flowering plants all year round. These plants often live in places without hard winters. In warm areas, hibiscus or certain kinds of geraniums can keep blooming. Houseplants, like African violets, can also flower indoors for months. They bring a bit of cheer no matter the weather outside.
Creating a Flowering Plants List
If you are planning a garden, it helps to create a flowering plants list. This list can help you pick plants for different colors. It can also help you choose plants for different seasons. A good list ensures you have blooms from spring to fall. This keeps the garden lively and beautiful for a long time.
Why Blooming Plants Are Important
Our Life Depends on Them
Blooming plants are not just nice to look at. They are absolutely vital for life on Earth. They are the base of the food chain. Animals eat plants. People eat plants and animals that eat plants. Without them, there would be no food.
The Air We Breathe
Plants also make the air we breathe. They take in carbon dioxide. They release oxygen as a waste product. This process is called photosynthesis. Every time a plant grows, it cleans the air. This is a crucial job that flowering plants do every single day.
Food for People and Animals
Most of the food we eat comes from these plants. Grains like wheat and rice are their seeds. Fruits like apples and oranges are their ripened ovaries. Vegetables like peas and beans are also parts of their life cycle. These are all flowering plants examples that feed the world.
Medicine and Other Uses
Plants also give us many other things. Many medicines come from certain plant parts. Wood for our homes and paper comes from flowering trees. Cotton for our clothes also comes from a blooming plant. They truly are some of the most helpful living things we have.
A Simple Answer to a Big Question
When asked what is a blooming plant, you can say it is life itself. It is a food source, an air cleaner, and a natural beauty. The simple answer covers a huge and important group of organisms. They are essential for a healthy planet.
Deep Dive into Plant Groups
Looking Closer at Types of Blooming Plants
To truly understand these organisms, we must look closer. The many types of blooming plants are divided in helpful ways. We can look at how they grow, where they grow, and how long they live. This helps us appreciate their wide range of survival tricks.
Annuals: Living for One Year
An annual plant lives for just one growing season. It goes from seed to flower to seed and then dies. Examples include marigolds and zinnias. They are great for adding quick, bright color to a garden. You have to replant them every year, but their beauty is worth it.
Biennials: The Two-Year Plan
Biennials have a life cycle that lasts two full years. In the first year, the plant grows roots and leaves. It gathers energy. In the second year, the plant flowers, makes seeds, and then dies. Carrots and foxgloves are examples of biennials. It is a patient way for blooming plants to reproduce.
Perennials: Coming Back Every Time
Perennials are the long-term residents of the garden. They live for many years. Their above-ground parts may die back in winter. However, the roots stay alive in the soil. They return to bloom again and again. Roses, hostas, and peonies are popular perennials. They give a garden stability.
Wildflowers and Cultivated Flowers
We can also group flowers by where they come from. Wildflowers grow on their own in nature. They are tough and survive without human help. Cultivated flowers are grown by people. They are often bred for brighter colors or bigger blooms. Both kinds are important flowering plants examples.
Understanding the Internal Structure
Features Beyond the Flower
The flowering plants characteristics are not only about the bloom. The roots, stems, and leaves are also very important. They all work together like a well-oiled machine. Understanding these parts helps us know how a plant stays healthy.
The Importance of Roots
The roots anchor the plant firmly in the ground. They also do the very important job of soaking up water. They take in minerals from the soil, too. This water and these minerals travel up the stem to the rest of the plant. Without strong roots, the whole plant cannot stand or eat.
Stems as the Plant’s Highway
The stem is like the highway of the plant. It carries water and food. The water goes up from the roots to the leaves. The food (sugar) made in the leaves goes down. The stem also holds up the leaves and flowers. It puts them in the best place to catch sunlight.
Leaves: The Food Factory
The leaves are where the magic happens. They contain a green chemical called chlorophyll. Chlorophyll captures the energy from the sun. Using sun energy, water, and carbon dioxide, the leaves make food. This is the process of photosynthesis we talked about earlier.
A Deeper Look at Plant Drawings
If you ever need to explain these parts, a flowering plants drawing is very helpful. It shows the roots, the stem, and the leaves. It also shows the flower at the top. This drawing is a simple way to teach the whole structure. It is a visual aid for understanding all these parts.
Learning the Reproduction Process in Detail
The Purpose of Pollen
Let’s look even closer at flowering plants reproduction. The male part of the flower is the stamen. It has an anther at the top. The anther is where the pollen is made. Pollen grains are very small. They hold the male genetic material. They must travel to the female part for a new seed to form.
The Receiving End: The Pistil
The female part is the pistil. The top of the pistil is the stigma. It is often sticky. Its job is to catch the pollen. Below the stigma is the ovary. The ovary holds the ovules, which are the plant’s eggs. The ovules become the seeds after fertilization happens.
Self-Pollination vs. Cross-Pollination
Pollination can happen in two ways. Self-pollination is when a plant’s pollen lands on its own stigma. Cross-pollination is when pollen travels from one plant to another. Cross-pollination is often better for plants. It mixes the genetic information. This makes the resulting blooming plants stronger and better able to survive.
How Seeds Are Formed
After the pollen lands, a tiny tube grows down into the ovary. This tube delivers the male part to the ovule. This is fertilization. The fertilized ovule then develops a hard coat. It becomes the seed. The ovary around it swells up and becomes the fruit. The simple flower has done its most important work.
Using a Diagram to Understand Steps
The full steps of the flowering plants life cycle are very clear in a good diagram. You can trace the pollen from the stamen to the pistil. You can see the ovule turn into a seed inside the ovary. A flowering plants diagram is a useful tool. It simplifies a complex natural process for all learners.
The Importance of Diversity
Why So Many Types of Blooming Plants?
Why are there so many types of blooming plants? The answer is survival. Over millions of years, plants have adapted. They changed to survive in different places. Some live in the cold. Others live in the desert. Each plant has a special way to attract its own pollinator. This creates huge plant diversity.
Adapting to Different Climates
Plants have developed ways to live in many climates. Succulents store water in their leaves to survive dry heat. Others, like the lilies, grow from bulbs underground. The bulbs keep them safe during freezing winters. The unique flowering plants characteristics allow them to thrive everywhere.
The Role of Color and Scent
The color and smell of flowers are not random. They are a signal. Bees like blue and yellow. Hummingbirds like red. Moths like white, strong-smelling flowers that bloom at night. These adaptations ensure the right animal visits. This is the amazing partnership that helps plants bloom.
More Flowering Plants Examples
Let’s think of more flowering plants examples to show the variety. The cactus flower is thick and waxy. It saves water. The water lily floats on the water. It uses the water to spread its seeds. The orchid is exotic and mimics insects to trick them into pollination. Every single flower tells a story of survival.
The Big Group: What Flowering Plants Are Called
Remember that all these diverse plants belong to one huge group. They are all called angiosperms. From the tallest trees to the smallest weeds, they all share that basic feature. They all make a flower to reproduce. Knowing this helps to group and understand them all.
Looking for Flowers All Year Long
Finding Blooms in Every Season
Gardeners and nature lovers enjoy finding flowering plants all season. It keeps the yard or nature trail interesting. Planning a garden for continuous blooms is a rewarding challenge. It means choosing plants that have different flowering times.
The Beauty of Perennial Flowers
To have a good mix, you need strong perennials. Some perennials flower early in spring. Others wait for the middle of summer. You can choose different kinds of perennials. This will make sure you always have plants blooming at any given time.
Adding Annuals for Constant Color
Annuals are also great for continuous color. They often bloom without stopping from spring until the first hard frost. Adding bright annuals to your flower beds fills the gaps. They are the perfect way to make sure you have flowering plants all year round in terms of color. They make the garden look fresh and alive.
Creating a Garden Bloom List
To make sure you don’t miss any blooms, you need a plan. Creating a detailed flowering plants list is the best way. You can divide the list into spring, summer, and fall bloomers. This plan is how smart gardeners keep the color going.
Plants That Love the Sun
Many plants need six or more hours of direct sun to flower well. Roses, daylilies, and petunias are sun lovers. They are beautiful blooming plants that need the light to perform their best. If you have a sunny spot, these plants are a great choice.
Understanding the Process Through Science
Flowering Plants Definition Biology Revisited
Let us look at the formal science again. The flowering plants definition biology sets the group apart from all others. It defines them by their unique way of reproduction. They form an ovary to protect the ovule. This is the main difference from other seed plants.
The Genetic Plan for the Life Cycle
The flowering plants life cycle is controlled by the plant’s genes. Genes are the instructions inside the plant’s cells. They tell the plant when to grow roots. They tell it when to grow leaves. Most importantly, they tell it exactly when to start to bloom. Changes in light and temperature can also trigger the blooming signal.
The Process of Seed Spreading
After the seed is ready, it needs to travel. This is called seed dispersal. Animals eat the fruit and carry the seeds far away. The wind catches light, fluffy seeds. Water can float some seeds to a new shore. This spreading ensures that blooming plants do not all crowd in one spot. This helps them find new places to grow.
The Role of Fruit in Protection
The fruit’s primary job is to protect the new seeds. It also helps with that travel. The delicious taste of a berry encourages an animal to eat it. The hard shell of a nut protects the seed inside. This protection is a key to the success of all flowering plants.
Illustrating Scientific Detail
When you study the parts and processes, it can get very complex. That is why a flowering plants drawing is an essential study aid. It clearly shows the ovary becoming the fruit. It shows the ovule becoming the seed. A visual image makes the science stick in your mind.
The Importance of Visual Learning
Making Complex Ideas Simple
The whole topic of plants can be hard to picture. We talk about cells, pollen, and ovaries. These parts are small and hidden. A good flowering plants diagram is like a map. It shows you the whole territory. It helps you see how the invisible parts work together.
Drawings for Students and Learners
Understanding the Life Cycle Visually
Imagine trying to explain the flowering plants life cycle without a drawing. It would be a long, dry explanation. A diagram shows the cycle in a circle. You see the seed. This visual flow is much easier to grasp for students.
Showing the Diversity of Types
We have talked about the many types of blooming plants. A collection of images or drawings can show their wide range. You can see the tiny flower of a cactus next to the huge bloom of a hibiscus. This visual comparison highlights the plant’s diverse world.
Creating Your Own Flowering Plants List
Choosing Annuals, Biennials, and Perennials
When making your list, keep the three life cycles in mind. Pick a few reliable perennials for long-term structure. Add some biennials for interesting bloom in the second year. Fill the rest of the space with bright annuals. This mix will give you flowering plants all season long.
Selecting the Right Colors
Color is an important part of a list. You might want a theme of warm colors (red, orange, yellow). You might prefer cool colors (blue, purple, pink). Planning the colors helps you create a beautiful view. Remember, all these colors come from blooming plants.
Finding Plants for Continuous Bloom
A specialised section of your list should focus on flowering plants all year round in your area. These are the plants that give you consistent colour. They are the stars of a low-maintenance garden. They are key to a successful, colourful landscape.
A Good List is a Good Plan
A carefully made flowering plants is a sign of a good plan. It shows you know the flowering plants you need. It helps you ensure you have a variety of types of blooming plants. This planning leads to a beautiful, successful garden.
The Secret of Year-Round Blooms
Achieving Continuous Color
Many people dream of having flowering plants all year round. While difficult in cold climates, it is possible to achieve continuous color. This is done by picking plants that bloom at different times. It is like passing a baton in a relay race.
Succession Planting
The key is called succession planting. When one group of flowers fades, the next group is just starting to bloom. Daffodils finish just as the irises begin. Irises finish as the roses begin. This constant cycle ensures you always have plants blooming.
Bringing the Outdoors Inside
In the deepest parts of winter, you can still have flowers. Bringing certain blooming plants indoors can help. African violets, orchids, and peace lilies are famous indoor bloomers. They ensure you have flowering plants all season, even when it’s snowing outside.
Choosing Long-Blooming Varieties
When selecting plants, look for varieties that have a long bloom time. Some roses will flower almost continuously if they are deadheaded. Deadheading means removing the old, faded flowers. This tricks the plant into making new ones. These are the workhorses of a flowering plants list.
The Rewards of a Year-Long Garden
Putting in the effort to choose the right types of blooming plants is worth it. You get to enjoy color and life no matter the month. The garden stays interesting. The wildlife, like the insects, have a consistent food supply. It is a beautiful and helpful effort.
Summary of Key Terms and Concepts
The Characteristics and Classification
We know that flowering plants characteristics include having vascular tissue. We also looked at flowering plants classification. This divides them into Monocots and Dicots. This system helps scientists organize the vast number of plant species.
The Full Life Story
We traced the complete flowering plants life cycle. It goes from a tiny seed to a mature plant. It includes the vital stage of flowering plants reproduction. This process ensures that new life is created year after year.
Looking at the List and Drawing
Remember the importance of the visual aids. A flowering plants diagram and a flowering plants drawing help you understand the parts. A carefully planned flowering plants list helps you make a great garden. These tools make learning about plants fun and easy.



Pingback: A World of Wonder: Unique Cross Breed Flowers & Modern hybrids
Pingback: Teaching Kids About Blooming Plants Fun & Easy Projects
Pingback: Perennial vs Annual Blooming Plants – Which One to Grow?.
Pingback: Why Your Plants Aren't Blooming